17. Optimization Solution & Samples
11 Optimization Solution Sampling V1
Forgotten: Scaling Step!
In the above training code, I forgot to include the scaling function for our real training images! Before passing in the images to our discriminator there should be a scaling step:
# important rescaling step
real_images = scale(real_images)This has been fixed in the exercise and solution notebooks in the classroom and the Github repository.
You should see a smoother decrease in Generator loss (as pictured below) with the addition of this line of code and slightly different-looking generated, sample images.
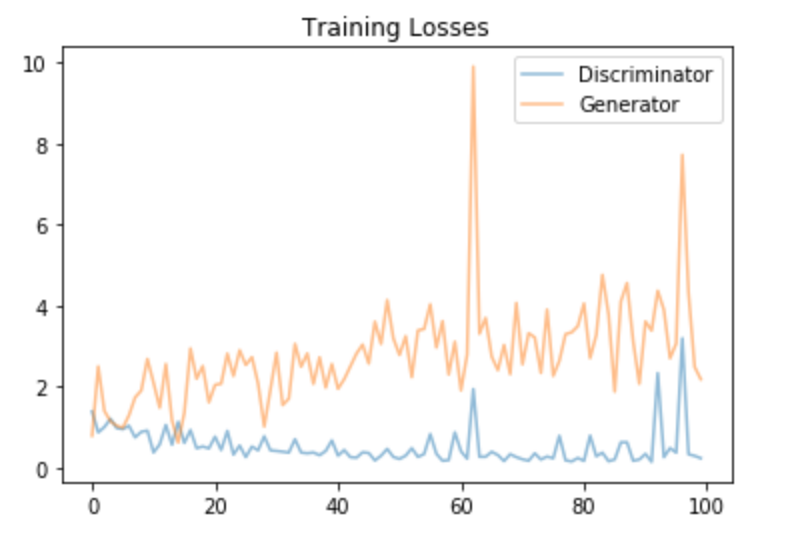
Actual training loss
In hindsight, I should have known that something was wrong with my training process due to the increasing and slightly unstable Generator loss in this video! For me, this is a good lesson in using a mix of intuition and training results to double check my work.
The correct scaling code and solution has been fixed in the in-classroom code and in the Github repo.
GANs for Illuminating Model Weaknesses
GANs are not only used for image generation, they are also used to find weaknesses in existing, trained models. The adversarial examples that a generator learns to make, can be designed to trick a pre-trained model. Essentially, small perturbations in images can cause a classifier (like AlexNet or a known image classifier) to fail pretty spectacularly!
This OpenAI blog post details how adversarial examples can be used to "attack" existing models, and discusses potential security issues. And one example of a perturbation that causes misclassification can be seen below.

Adding a small amount of noise to an image of a panda causes a model to misclassify it as a gibbon, which is a kind of ape. One of the interesting parts of this is the model's confidence. With this noise it is 99.3% confident that this is an image of a gibbon, when we can pretty clearly see that it is a panda!